Sending Arbitrary SMS over NAS Messages with an Extended srsUE
Previous articles 1 and 2 demonstrated short message service (SMS) over Non-Access Stratum (NAS) in private and commercial mobile networks. In these demonstrations, messages were sent according to the specifications of the operating system (OS) and modem of mobile devices. To investigate the actual behavior of SMS over NAS in more detail, it is necessary to have the capability to send messages that are not constrained by device vendors’ specifications. Therefore, this article extends the capability of srsUE to send arbitrary SMS over NAS messages.
Note
The extended srsUE, which supports SMS sending as well as receiving and various sending options, can be checked out from GitHub as “smsUE”: https://github.com/atsunoda/smsUE
Summary
By extending the open-source implementation of srsUE, SMS over NAS messages can be sent on 5G mobile networks. As srsUE supports connections to both 4G and 5G networks, it can transfer data at the NAS layer. To send SMS over NAS messages, part of the connection process to the core network (CN) in srsUE has been modified and a function for sending messages has been added after the registration procedure. A message sent from this function was successfully received by an SMS client app on an Android device, as demonstrated in a private 5G mobile network.
Necessity and Limitation of SMS Sending Capability
To investigate the actual behavior of SMS over NAS, it is necessary to manipulate data not visible to users in general message exchange. In SMS client apps, users can only input values such as a destination phone number and message text. This means that only certain parts of an SMS Protocol Data Unit (PDU) can be manipulated. Figure 1 illustrates the control plane protocol stack shown in 3GPP TS 38.300¹, which defines the 5G radio interface protocol architecture, with the addition of SMS. To investigate the behavior of the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) and the Short Message Service Function (SMSF), which control SMS over NAS in the CN, it is necessary to manipulate the SMS PDUs and the underlying NAS messages.
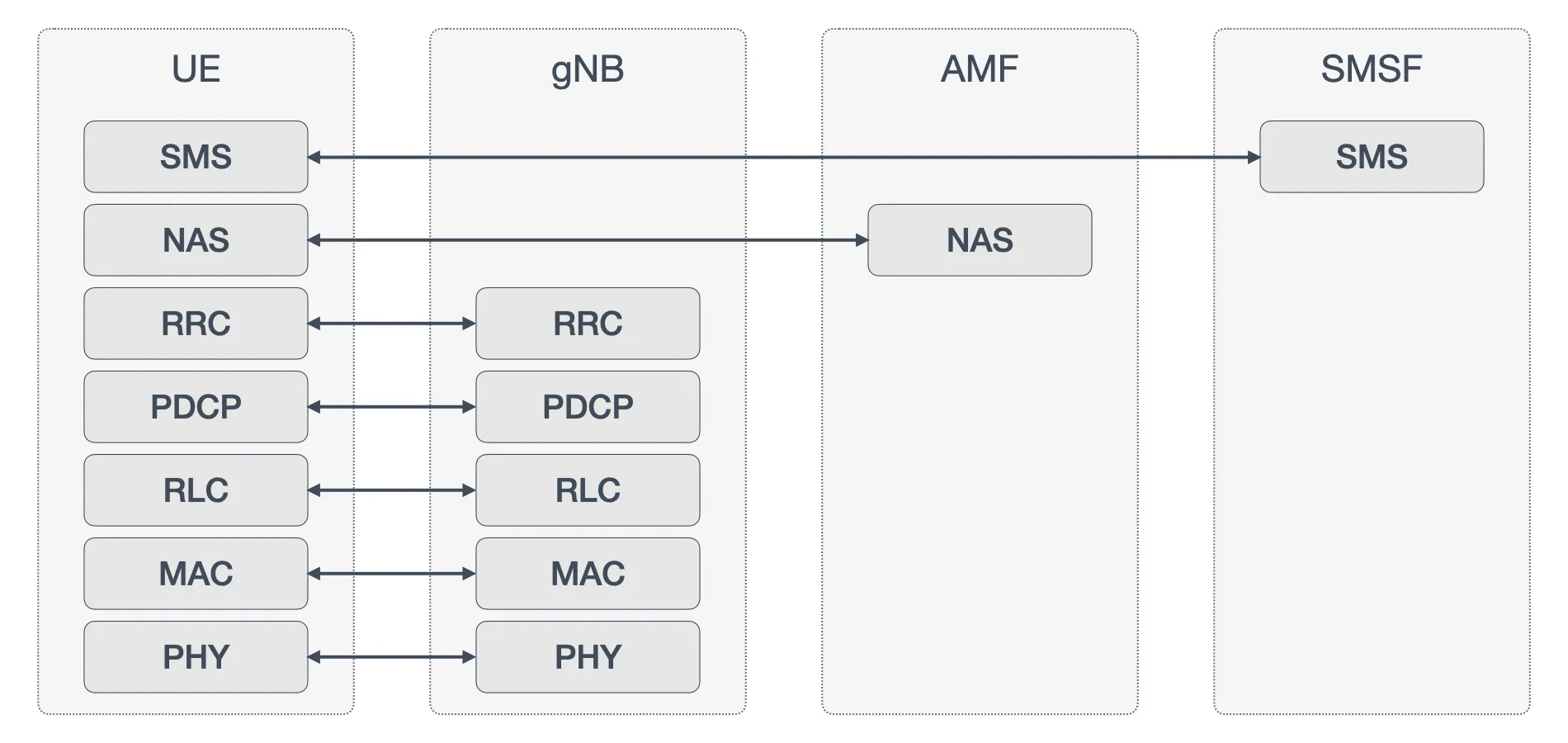
However, mobile devices are limited in their SMS sending capabilities. SMS client apps installed on mobile devices send messages using APIs provided by OSs such as Android and iOS. Android exchanges data with the modem through an abstraction layer called the Radio Interface Layer (RIL), while iOS uses a layer called CommCenter². NAS layer communications are handled internally within the modem. Therefore, manipulating NAS messages before they are sent from mobile devices requires the use of tools provided by the modem vendor or rewriting the modem firmware³. As noted in a previous article, even if root privileges are obtained on the OS to access non-public APIs, or if AT commands are used to access the modem directly, the scope of manipulation is limited to the SMS PDUs.
Extension of SMS Sending Capability to srsUE
To send arbitrary SMS over NAS messages, srsUE has been extended. srsUE is an open-source UE modem provided by the srsRAN project⁴, with connectivity capabilities for both 4G and 5G networks. Specifically, srsUE connects to a base station via the Radio Resource Control (RRC) layer, then registers with a CN via the NAS layer, establishes a data session, and obtains an IP address. srsUE connection process is implemented independently for 4G and 5G, and only the 5G implementation has been extended. Therefore, this extension only supports SMS over NAS provided in 5G networks.
The srsUE has been extended to send SMS over NAS messages after completing the registration procedure with the CN. SMS over NAS is forwarded in the control plane, allowing UEs to send messages before establishing a data session. Figure 2 shows the sequence of the extended srsUE connection process. After establishing an RRC connection with the gNB, the srsUE sends a Registration Request message to the AMF (Step 1 in Figure 2). This triggers the AMF to authenticate the srsUE’s subscriber information and register it with the SMSF, as shown in Figure 8 of the previous article. The AMF then sends a Registration Accept message to the srsUE, and the srsUE responds with a Registration Complete message (Steps 2 and 3 in Figure 2). The srsUE then sends an Uplink NAS transport message loaded with an SMS PDU to the AMF (Step 4 in Figure 2). This step has been added by the extension.
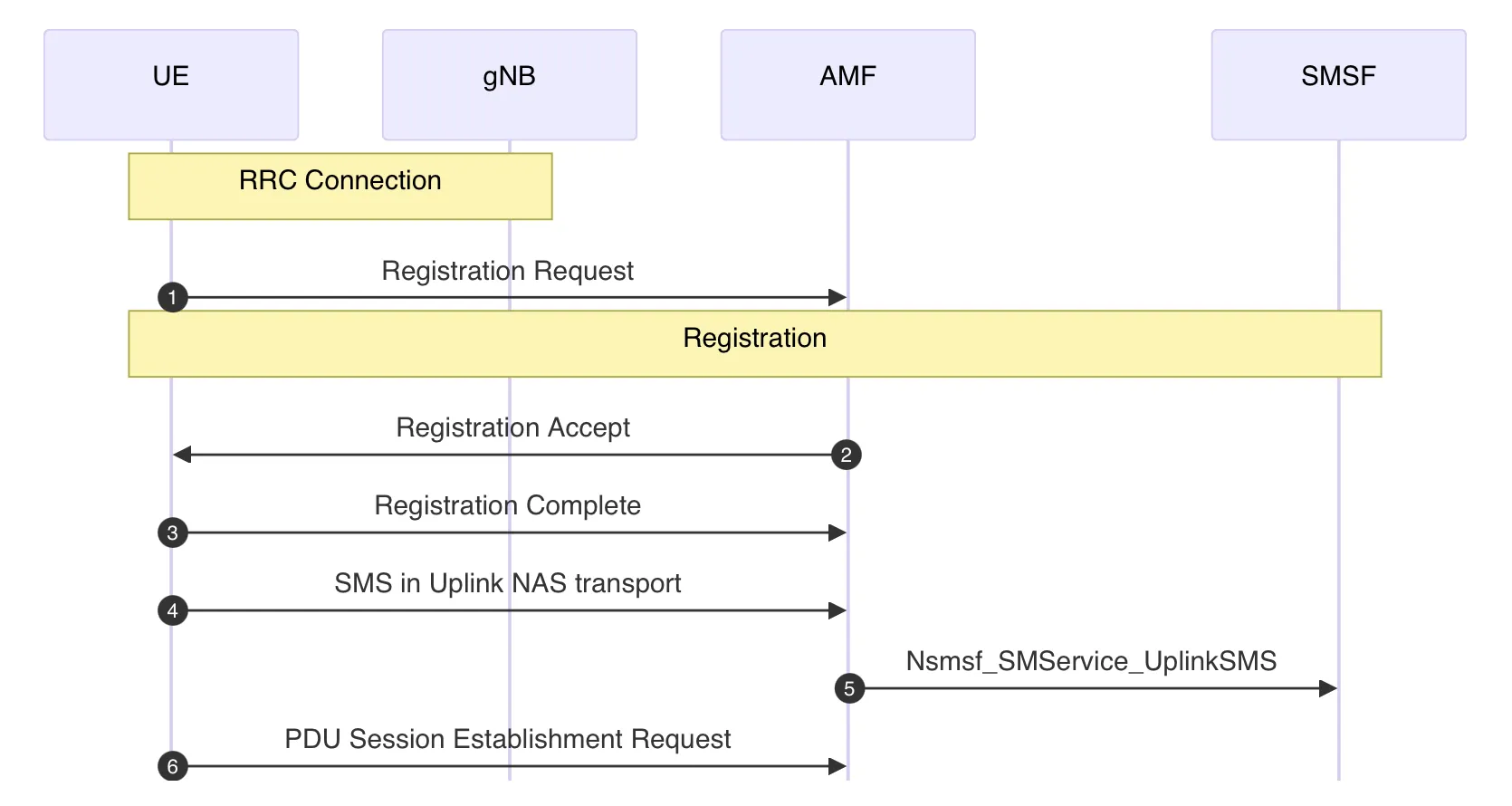
Before sending SMS, the UE must request and be allowed to use SMS from the CN in the registration procedure. According to 3GPP TS 24.501⁵, which defines the NAS specification for the 5G System (5GS), in order to use SMS in the 5GS, the UE must set SMS over NAS supported in the 5GS update type element of the Registration Request message, and the AMF must set SMS over NAS allowed in the 5GS registration result element of the Registration Accept message. Since the srsUE sets SMS over NAS not supported in the 5GS update type element within the send_security_mode_complete() function in nas_5g.cc, it has been changed to SMS over NAS supported as shown in Figure 3.
modified_registration_request.update_type_5gs.sms_requested.value =
- update_type_5gs_t::SMS_requested_type::options::sms_over_nas_not_supported;
+ update_type_5gs_t::SMS_requested_type::options::sms_over_nas_supported;
The SMS sending process has been added to run after the registration procedure is complete. When the srsUE receives the Registration Accept message from the AMF, it executes the handle_registration_accept() function in nas_5g.cc. At the end of this function, it calls the send_registration_complete() function to send the Registration Complete message, and then calls the trigger_pdu_session_est() function to initiate the establishment of the PDU session. The send_sms_over_nas_message() function, which executes the SMS sending process, has been added to be called after the send_registration_complete() function is executed, as shown in Figure 4.
int nas_5g::handle_registration_accept(registration_accept_t& registration_accept)
{
...
if (send_reg_complete == true) {
send_registration_complete();
+ send_sms_over_nas_message();
}
// TODO: use the state machine to trigger that transition
trigger_pdu_session_est();
return SRSRAN_SUCCESS;
}
The send_sms_over_nas_message() function, which executes the SMS sending process, has been added to nas_5g.cc. Figure 5 shows the code for this function. In the case of SMS over NAS, since an SMS PDU is encapsulated in the payload of an Uplink NAS transport message, the payload_container_type is set to sms. The SMS PDU to be sent is loaded into the payload_container_contents. The byte sequence in Figure 5 corresponds to the SMS PDU shown in Figure 13 of the previous article. The constructed Uplink NAS transport message is finally passed to the RRC layer as a Service Data Unit (SDU) and transmitted over the air.
int nas_5g::send_sms_over_nas_message()
{
unique_byte_buffer_t pdu = srsran::make_byte_buffer();
if (!pdu) {
logger.error("Couldn't allocate PDU in %s().", __FUNCTION__);
return SRSRAN_ERROR;
}
nas_5gs_msg nas_msg;
nas_msg.hdr.security_header_type = nas_5gs_hdr::security_header_type_opts::integrity_protected_and_ciphered;
nas_msg.hdr.sequence_number = ctxt_base.tx_count;
ul_nas_transport_t& ul_nas_msg = nas_msg.set_ul_nas_transport();
ul_nas_msg.payload_container_type.payload_container_type.value =
payload_container_type_t::Payload_container_type_type_::options::sms;
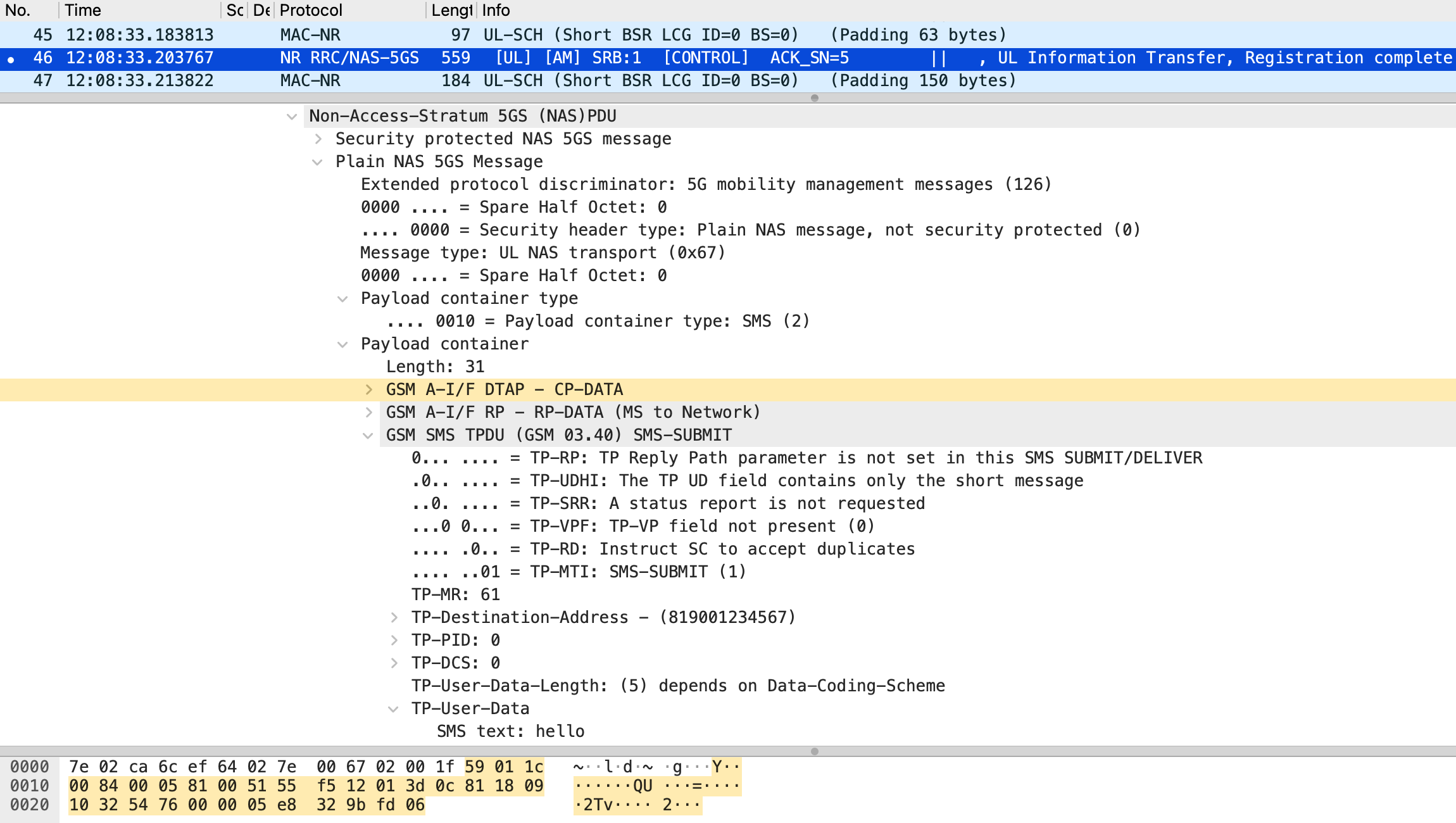
unsigned char bytes[] = {0x59, 0x1, 0x1c, 0x0, 0x84, 0x0, 0x5, 0x81, 0x0, 0x51, 0x55, 0xf5, 0x12, 0x1, 0x3d, 0xc, 0x81, 0x18, 0x9, 0x10, 0x32, 0x54, 0x76, 0x0, 0x0, 0x5, 0xe8, 0x32, 0x9b, 0xfd, 0x6};
ul_nas_msg.payload_container.payload_container_contents.resize(sizeof(bytes));
std::copy(std::begin(bytes), std::end(bytes), ul_nas_msg.payload_container.payload_container_contents.begin());
if (nas_msg.pack(pdu) != SRSASN_SUCCESS) {
logger.error("Failed to pack UL NAS transport.");
return SRSRAN_ERROR;
}
cipher_encrypt(pdu.get());
integrity_generate(&ctxt_base.k_nas_int[16],
ctxt_base.tx_count,
SECURITY_DIRECTION_UPLINK,
&pdu->msg[SEQ_5G_OFFSET],
pdu->N_bytes - SEQ_5G_OFFSET,
&pdu->msg[MAC_5G_OFFSET]);
if (pcap != nullptr) {
pcap->write_nas(pdu.get()->msg, pdu.get()->N_bytes);
}
logger.info("Sending SMS message in UL NAS transport.");
rrc_nr->write_sdu(std::move(pdu));
ctxt_base.tx_count++;
srsran::console("Sending SMS over NAS message.\n");
return SRSRAN_SUCCESS;
}
Demonstration of the Extended srsUE
The extended srsUE was demonstrated on a private 5G mobile network. The demonstration reused the mobile network described in the previous article and the subscriber information shown in a different previous article. The srsUE was used as the sender of the SMS over NAS message and the Pixel 6 was used as the receiver. Therefore, the srsUE was assigned the IMSI 001010000000001 and the phone number 818001234567, while the Pixel 6 was assigned 001010000000002 and 819001234567. Two USRP B205mini-i⁶ were used as the radio hardware for the gNB and the srsUE. As shown in Figure 6, these devices were placed inside a shielded box during the demonstration.
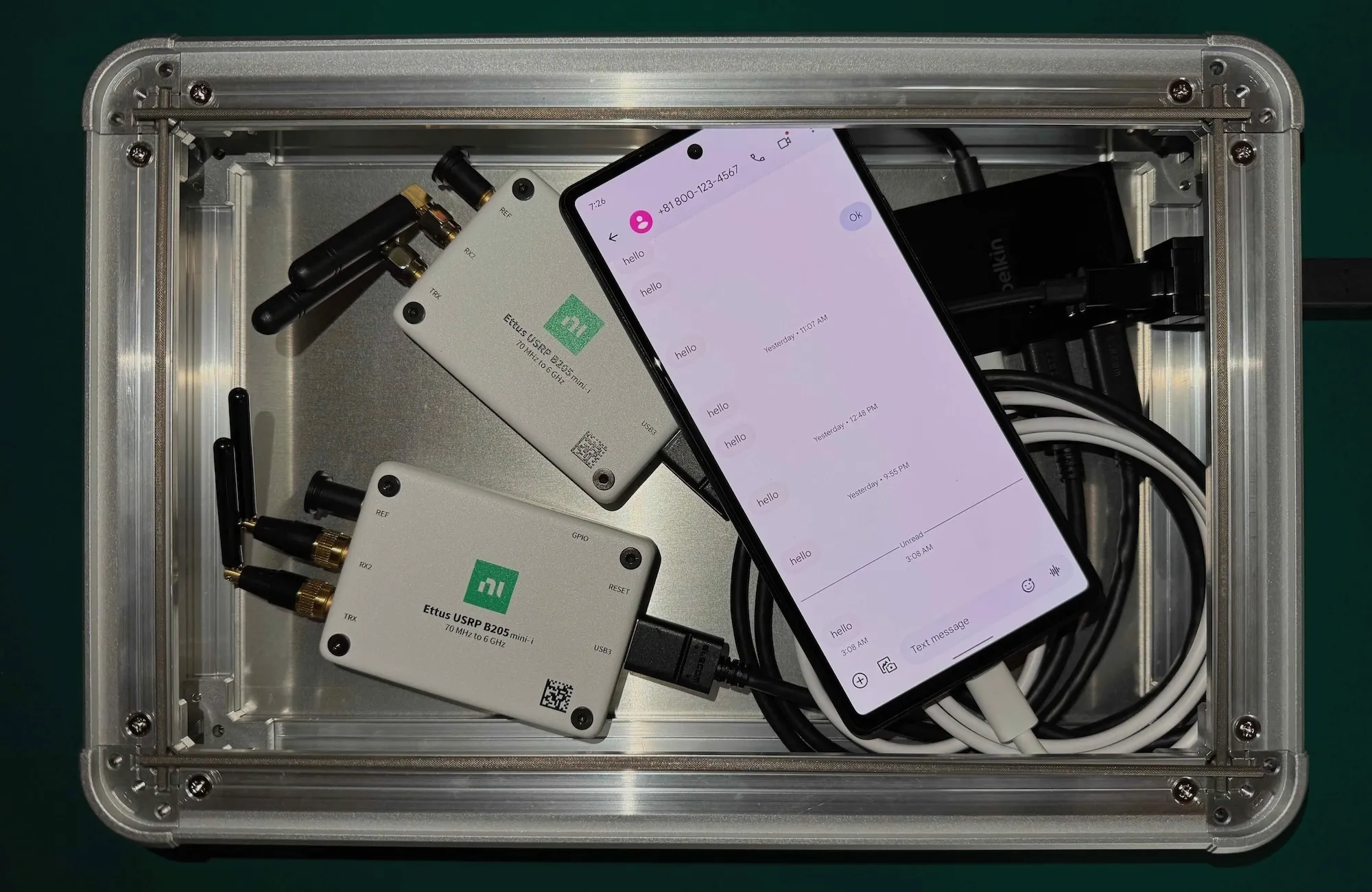

The demonstration of the extended srsUE sending the SMS over NAS message is shown in Figure 7. In the figure, the srsUE is running in a terminal after the Pixel 6 has connected to the mobile network. The srsUE sends the message after completing the registration procedure with the CN, and the Pixel 6 receives it. The Pixel 6 displays the srsUE’s phone number 818001234567 as the originating number of the received message. By analyzing the packets captured during the demonstration, it is confirmed that the srsUE sends the SMS over NAS message as expected.
First, the extended srsUE is confirmed to support SMS over NAS. As shown in Figure 3, the srsUE has been modified to inform the CN that it supports SMS over NAS in the Registration Request message. In the Registration Request message captured on the srsUE, the 5GS update type element is set to SMS over NAS transport requested (SMS requested): Supported, as shown in Figure 8. Consequently, in the Registration Accept message, the 5GS registration result element is set to SMS over NAS: Allowed, as shown in Figure 9. These results mean that the extended srsUE is allowed by the CN to use SMS over NAS.
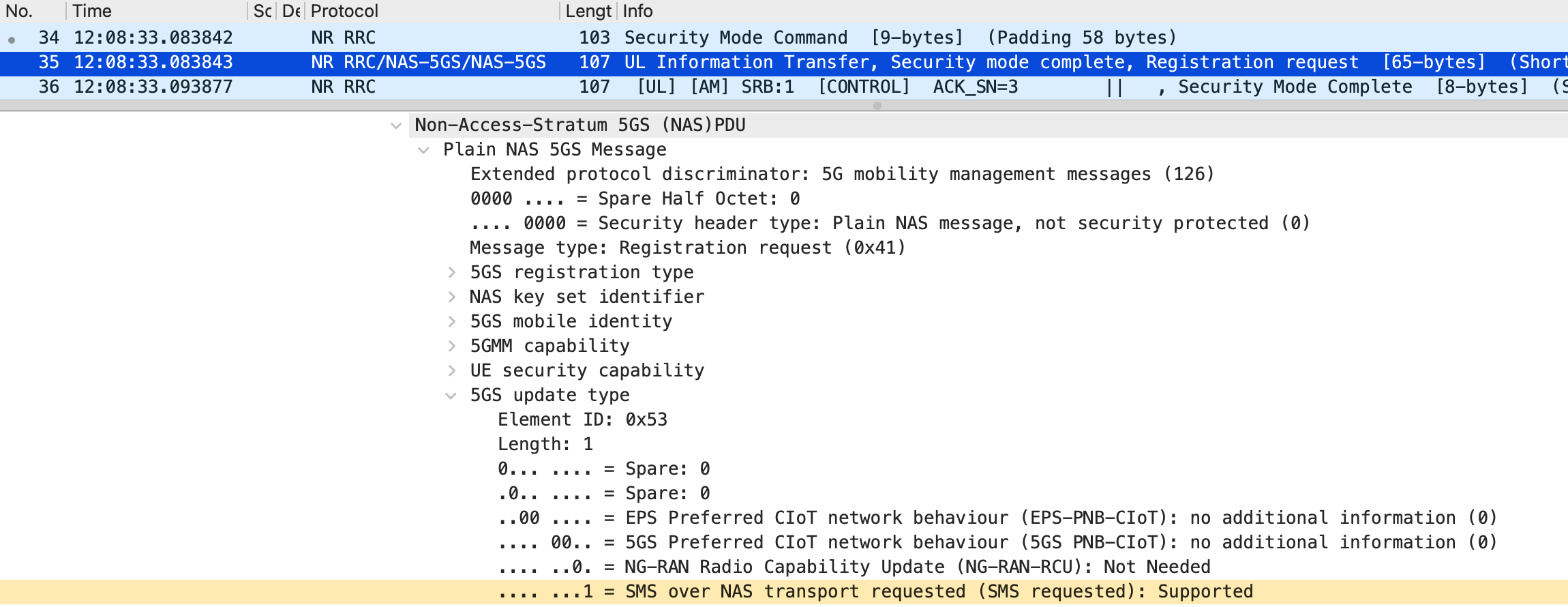
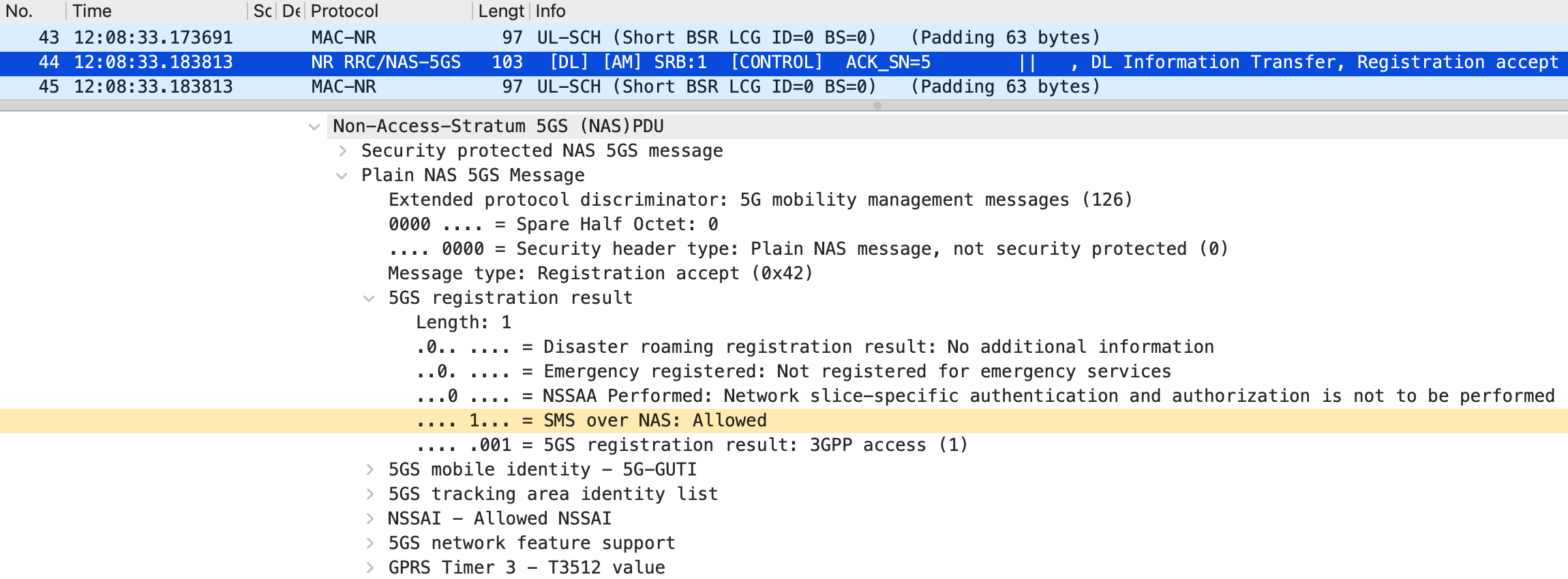
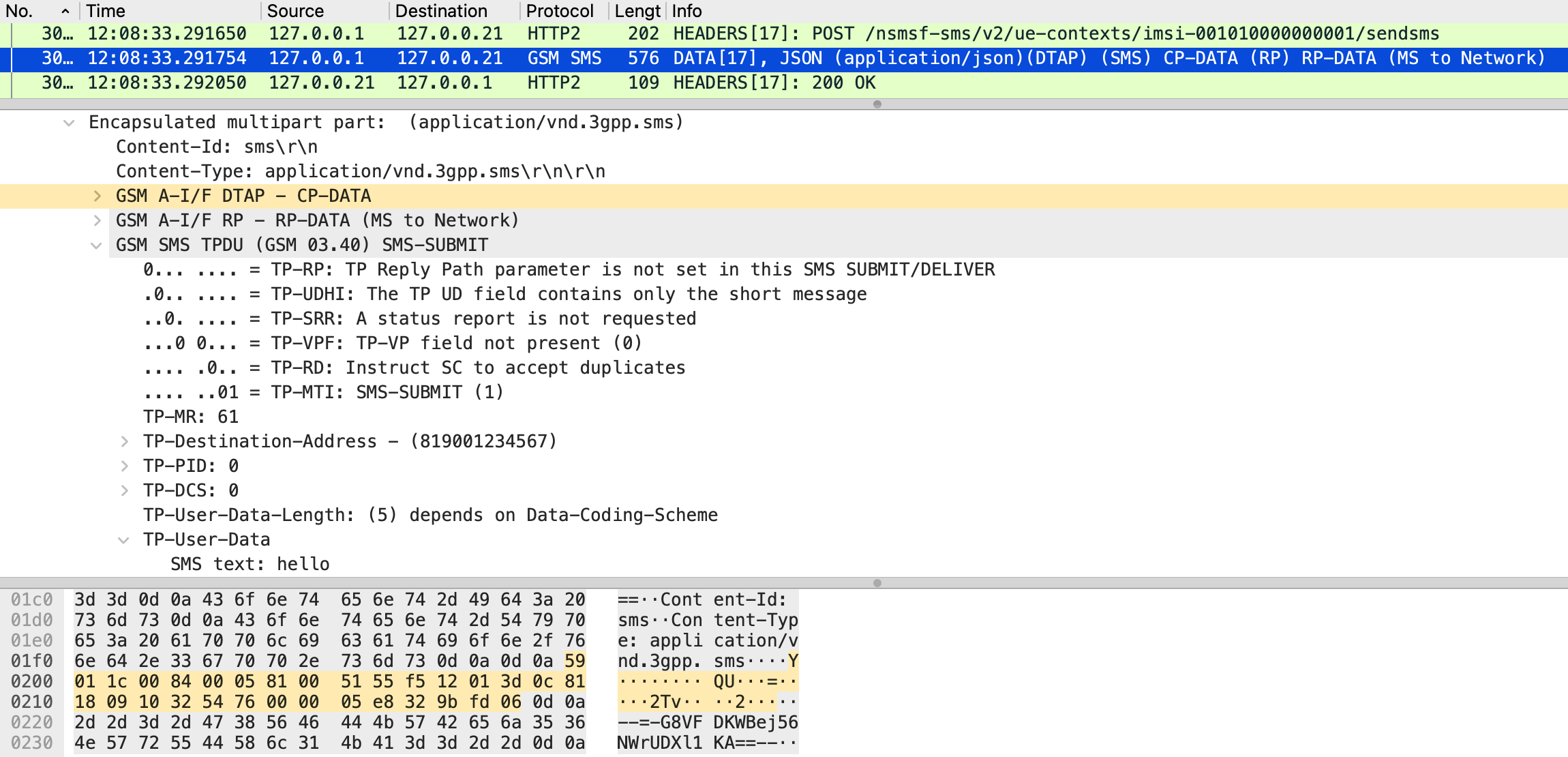
Next, the extended srsUE is confirmed to send SMS over NAS messages as expected. As shown in Figure 5, the srsUE loads the byte sequence representing the SMS PDU into the payload of the Uplink NAS transport message. In the captured Uplink NAS transport message, the byte sequence is interpreted as the SMS PDU, as shown in Figure 10. Furthermore, in the Nsmsf_SMService_UplinkSMS request from AMF to SMSF captured in the CN, the byte sequence matches as shown in Figure 11. Based on these results, it is concluded that the srsUE sends SMS over NAS messages as implemented.
Conclusion and Future Work
By extending the open-source implementation of srsUE, the SMS sending capability on 5G mobile networks has been added. This extension allows sending arbitrary SMS over NAS messages that are difficult to send from mobile devices. Since this extension was implemented for research purposes, it does not have the capabilities expected from SMS client apps, such as receiving messages. It also does not have the capability to modify messages or send multiple messages. Further extension of these capabilities can be useful for investigating mobile network features related to SMS.
¹ 3GPP TS 38.300, NR; NR and NG-RAN Overall description; Stage-2
² Tobias Kröll. 2021. ARIstoteles: iOS Baseband Interface Protocol Analysis
³ Carsten Bruns. 2021. Modification of LTE Firmwares on Smartphones
⁴ UE User Manual - srsRAN 4G 23.11 documentation
⁵ 3GPP TS 24.501, Non-Access-Stratum (NAS) protocol for 5G System (5GS); Stage 3
⁶ USRP B205mini-i - Ettus Research, a National Instruments Brand